[comment]: # (mdslides presentation.md --include media) [comment]: # (The list of themes is at https://revealjs.com/themes/) [comment]: # (The list of code themes is at https://highlightjs.org/) [comment]: # (markdown: { smartypants: true }) --- <style type="text/css"> .reveal { font-size: 2.2em; } .reveal .code-wrapper code { white-space: pre; font-size: 2em; line-height: 1.2em; } </style> ---  <img src="media/int.png" width="8%"> DevOps Bootcamp - INT College & UPES University # Elastic Load Balancing 
### Today's agenda - Load balancer motivation - Listeners and target groups - Application load balancers
### Load Balancers - from clients and routes requests to its registered targets. - Targets may be EC2 instances, containers, and IP addresses - LB monitors the health of its registered targets and ensures that it routes traffic only to healthy targets. - LB can map requests across different availability zones in a single region 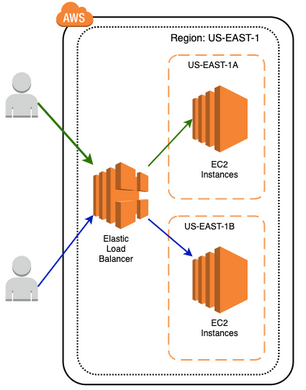
### Listeners and Target Groups - To configure your load balancer, you create **target groups**, and then register targets with your target groups. - You also create **listeners** to check for connection requests from clients, and listener rules to route requests from clients to the targets in one or more target groups. - You can use an HTTPS listener to offload the work of TLS encryption and decryption to your load balancer. 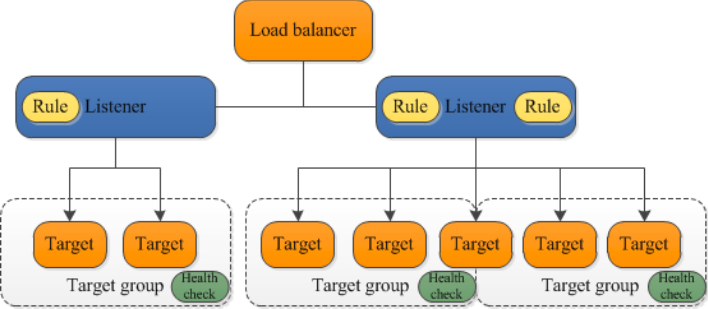
### Load balancer scheme - Before a client sends a request to your LB, it resolves the load balancer's DNS. Amazon DNS servers return one or more IP addresses to the client. These are the IP addresses of the **load balancer nodes** for your load balancer. - The client determines which IP address to use to send requests to the load balancer. The load balancer node that receives the request, selects a healthy registered target and sends the request to the target using its private IP address. 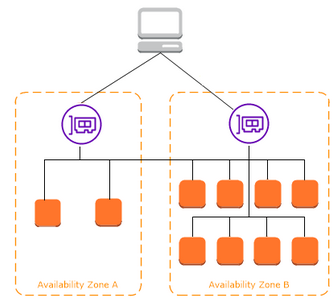
### Load balancer scheme - When you create a load balancer, you must choose whether to make it an internal load balancer or an internet-facing load balancer. - The nodes of an internet-facing load balancer have public IP addresses. The DNS of an internet-facing load balancer is publicly resolvable to the public IP addresses of the nodes. - The nodes of an internal load balancer have only private IP addresses. The DNS of an internal load balancer is **publicly resolvable** to the private IP addresses of the nodes. - Both internet-facing and internal load balancers route requests to your targets using private IP addresses.
### Application Load Balancer - The Application Load Balancer distributes incoming HTTP and HTTPS traffic across multiple targets, as follows: 1. Your client makes a request to your application. 2. The listeners in your load balancer receive requests matching the protocol and port that you configure. 3. The receiving listener evaluates the incoming request against the rules you specify, and if applicable, routes the request to the appropriate target group. 4. Healthy targets in one or more target groups receive traffic based on the load balancing algorithm, and the routing rules you specify in the listener. 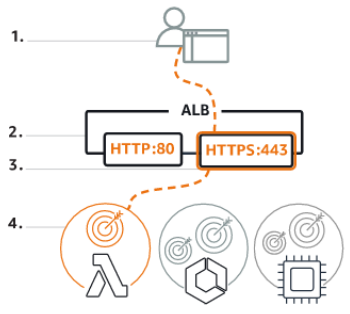
### ALB and HTTP headers - The `X-Forwarded-For` request header helps you identify the IP address of a client when you use an HTTP or HTTPS load balancer. - The `X-Forwarded-Proto` request header helps you identify the protocol (HTTP or HTTPS) that a client used to connect to your load balancer. - The `X-Forwarded-Port` request header helps you identify the destination port that the client used to connect to the load balancer.
### Sticky sessions for the ALB - By default, an ALB routes each request independently to a registered target based on the chosen load-balancing algorithm. - Sticky session ensures that all requests from the user during the session are sent to the same target. - This feature is useful for servers that maintain state information in order to provide a continuous experience to clients. To use sticky sessions, the client must support cookies.
### Cross-zone load balancing - When cross-zone load balancing is enabled (by default in ALB), each load balancer node distributes traffic across the registered targets in all enabled Availability Zones. - When cross-zone load balancing is disabled (can be done only in NLB), each load balancer node distributes traffic only across the registered targets in its Availability Zone. 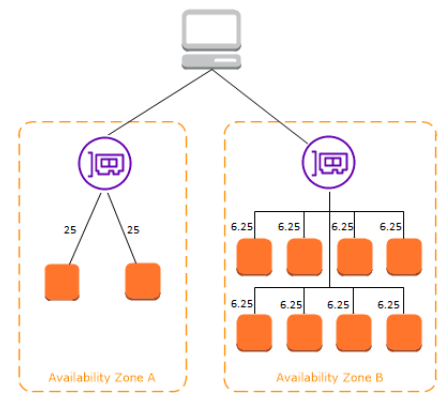
# Thanks